Projects
| Blockchain technology develops static smart contracts for decentralized business transactions, lacks dynamic decision making capabilities that limits the possibilities of ever-increasing demands of business applications. Artificial intelligence, a computational prediction platform provides intelligent predictions, actions, recognition that lacks the ability to hold on to integrity of the prediction result and require help of external authorities to secure the system. Blockchain based AI prediction can cover the gaps of individual technologies and can mutually benefit from one another to develop a decentralized machine learning architecture that promises to yield better security, automation and dynamism of the application. This work naive Bayes algorithm that overcomes the hurdles and promises to open up more opportunities in the field of Blockchain-AI decentralized applications. | 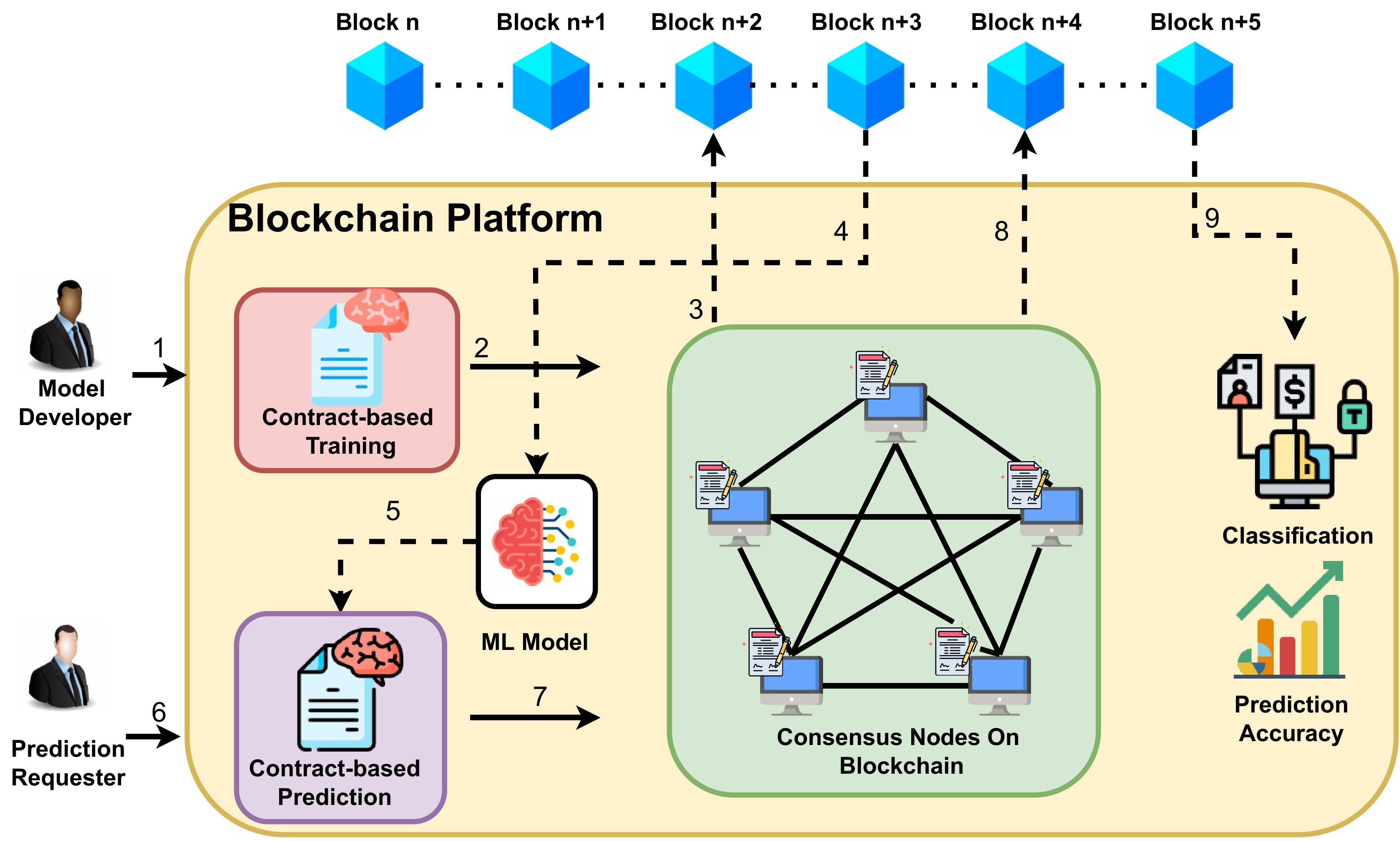 |
| Smart contract languages cannot perform model-based predictions due to the absence of floating-point operations required by activation functions of neural networks. In this work, we derive a novel method using the Taylor series expansion to compute the floating-point equivalent output for activation functions. We train the deep learning model off-chain using a standard Python programming language. Moreover, we store models and predict on-chain with blockchain smart contracts to produce a trusted forecast. Our experiment and analysis achieved an accuracy (99\%) similar to popular Keras Python library models for the MNIST dataset. | 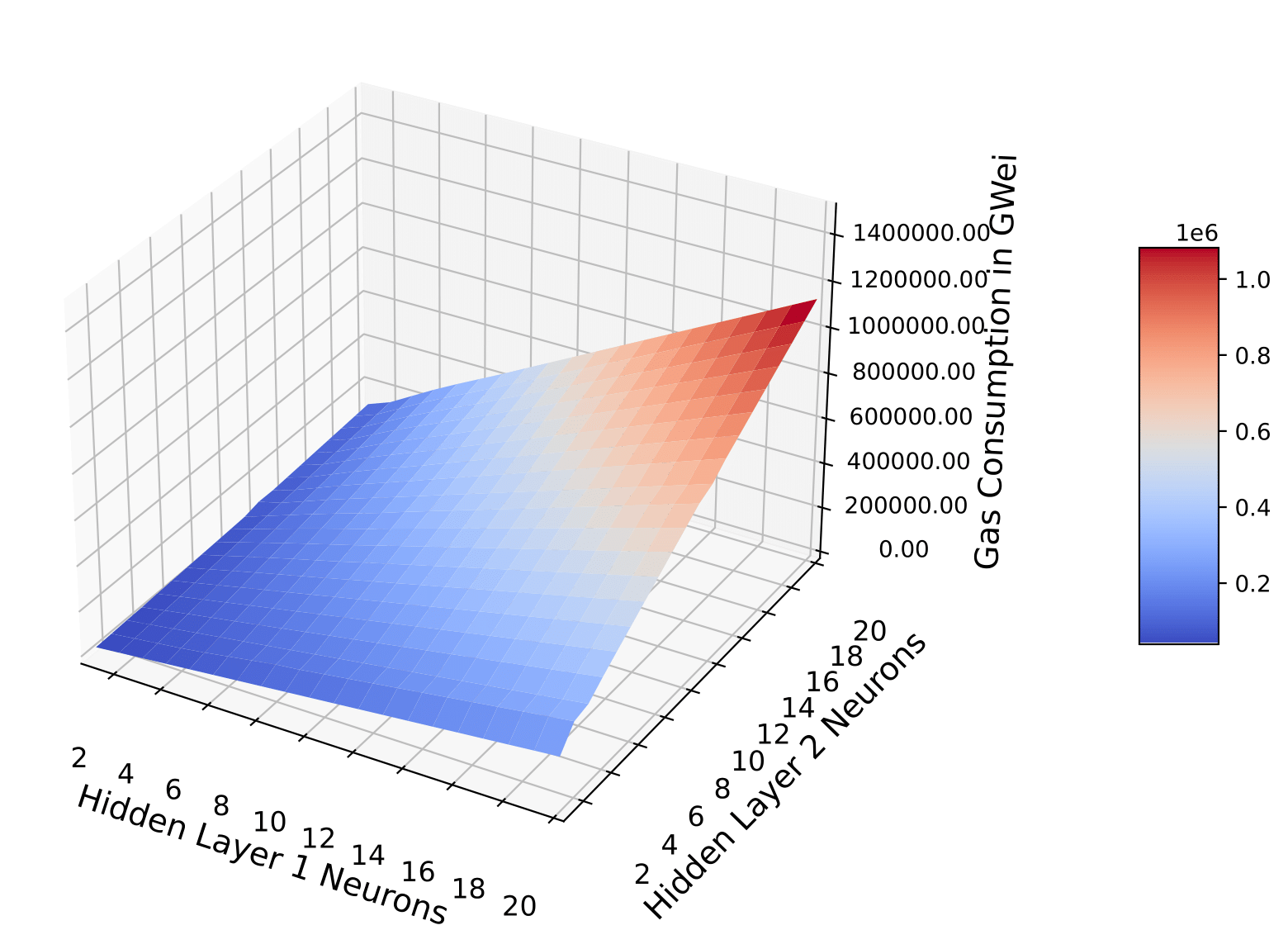 |
| Current consensus algorithms do not address the requirements of high-stake applications that demand unanimous consensus with deliberation. For instance, a trial case at a court requires unanimous consensus to decide the fate of a criminal. With limited agreement structure and no deliberation, the current consensus protocol cannot handle the consensus problem. Our research determines the requirements of a deliberative unanimous consensus model for high-stake applications. Moreover, we propose a family of consensus models that agree on the answer’s correctness and the methods used to reach it. | 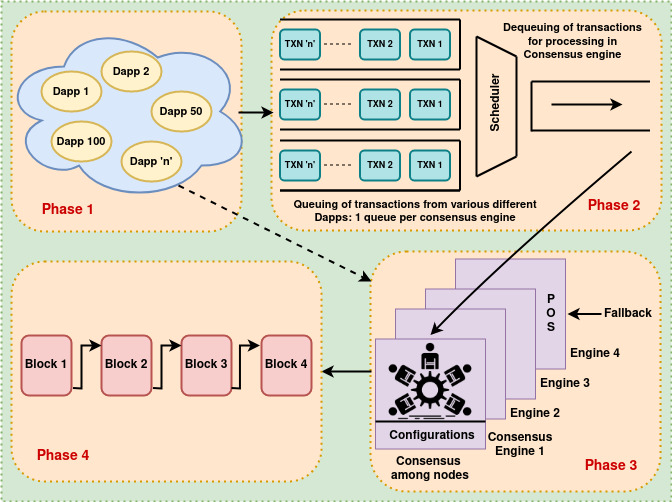 |
| Data cooperative (called “data coop” for short) is an emerging approach in the area of secure data management. It promises its users a better protection and control of their data, as compared to the traditional way of their handling by the data collectors (such as governments, big data companies, and others). However, for the success of data coops, existing challenges with respect to data management systems need to be adequately addressed. Especially, they concern terms of security and privacy, as well as the power imbalance between providers/owners and collectors of data. Designing a security and privacy model for a data coop requires a systematic threat modeling approach that identifies the security landscape, attack vectors, threats, and vulnerabilities, as well as the respective mitigation strategies. In this paper, we analyze the security of data cooperatives, identify potential security risks and threats, and suggest adequate countermeasures. We also discuss existing challenges that hinder the widespread adoption of data coops. | 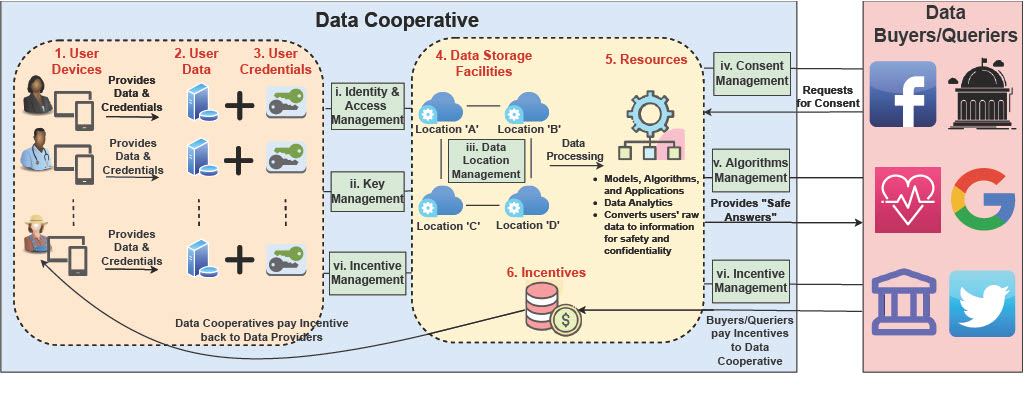 |
Metaverse is an integration of many different technologies like blockchain, AI, edge computing, virtual reality, and many more, simulating the physical world in a virtual environment with holograms and avatars representing individuals. The metaverse is still in the early developmental stages as various tech companies propose exciting and promising features the technology can offer. Despite the plethora of benefits, this can bring to its users, for it to be able to achieve its potential, the security of the digital infrastructure and assets needs to be carefully addressed. In this paper, we present the metaverse and the collection of technologies it comprises. We focus on the integrated auditing methodology of the metaverse in detail that requires multimodal deep learning, which incorporates blockchain-based smart contracts as well. We provide attention to identifying major security threats and vulnerabilities in the decentralized metaverse, which, in our opinion, may hinder the success of the metaverse. Finally, we conclude by proposing mitigation strategies for the discussed security threats via integrated multimodal deep learning and smart contract audit for the presented security vulnerabilities for the metaverse.
Decision Trees to Help Smart Contracts to Predict for Machine Learning Algorithms
Blockchain helps AI to build trustworhty and immutable predictions system. To further study the nature of smart contract problems and their limitations to predict using machine learning algorithm, we need to investigate. Decision Tree algorithm and evaluate the mathematical model for smart contracts to help the prediction algorithms. Building Decision Trees require the computation of entropy and information gain to identify the best. feature with best split to create the decision tree. We will derive the necessary equations to compute the complex mathematical equations and implement them inside the smart contract. Moreover, the blockchain is expensive for layer one computations. The layer two scalability options are good in terms of speed but not secure enough. We will use layer one scalability options for our algorithm and record the performance evaluation.
BLOCKAI Trustmeter: A Guide to Quantify The Trust of AI in Decentralized Ledger
The quest to help AI Algorithms through blockchain platform demands proofs that blockchain helps build trust in securing AI algorithms. Detering model poisoning attack is discussed in many academic articles. However, the methods that secure the models from poisoning are mostly theoretical that does not guarantee trust in the cognitive formulae. The blockchain platforms are creating footprints everywhere making data in applications tamper-proof. Some of the applications have clear benefits for using blockchain. Financial transactions are a major user of blockchain technology that protects against centralized threats. Complex applications from Artificial Intelligence are driving towards blockchain-based prediction system, but many are unware about how could blockchain help AI? This research focuses on the qunatitative analysis of security enhancement that blockchain provides to AI algorithms. This will include the security abalysis of non-blockchain versus blockchain-based prediction system




